Focus on the core values of business
With SINNOTECH, we guarantee the best experience

What is Harmful Gas Remote Management System?
The Confined Space Harmful Gas Remote Monitoring System is a digital-based industrial
safety management system that targets confined spaces such as manholes with a high fatality rate due
to high-risk work to secure worker safety from suffocation accidents and improve work efficiency,
and to actively prevent accidents and respond to accidents quickly.
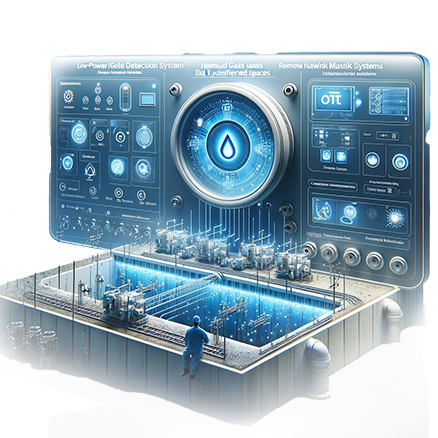


Wireless Harmful Gas Telemetry System
IoT wireless-based low-power confined space harmful gas telemetry devices with
SINNOTECH's patented low-power technology are optimized for building a harmful gas remote management
system that performs regular monitoring of harmful gas concentrations on remote SCADA servers without external
power supply, utilizing only batteries for operation, is easy to install, low cost, and performs periodic
measurement and transmission functions, and is currently applied in confined spaces such as manholes
in water supply networks and can be applied to various industries where confined space hazards persist.
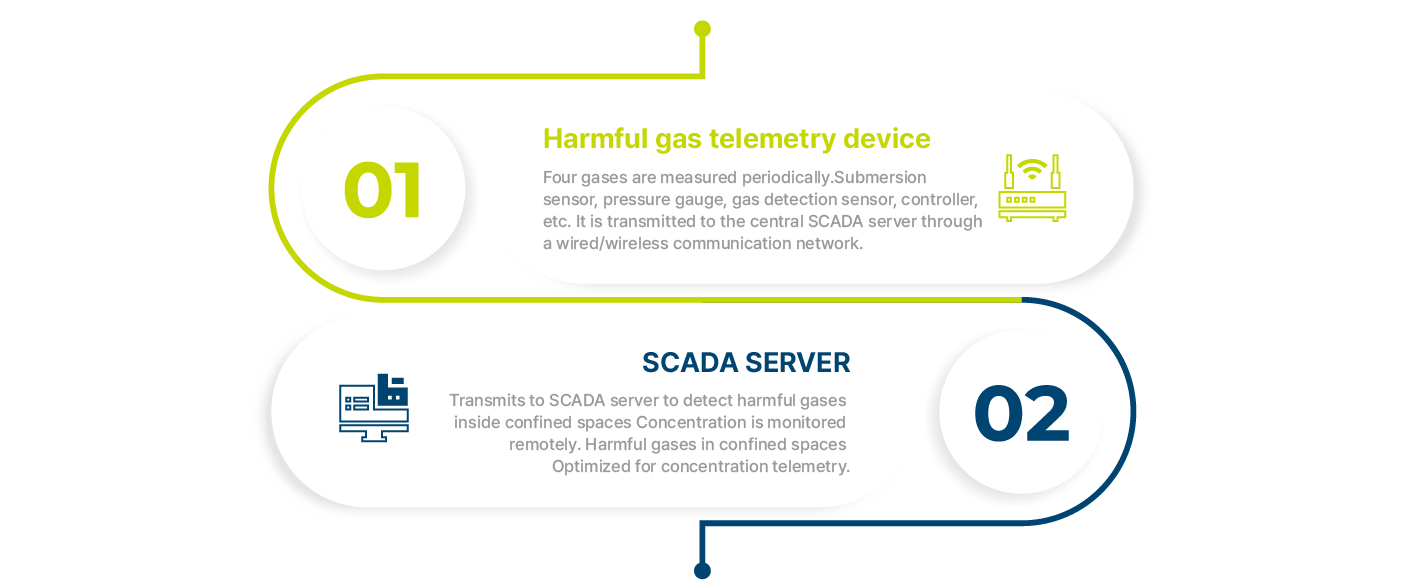
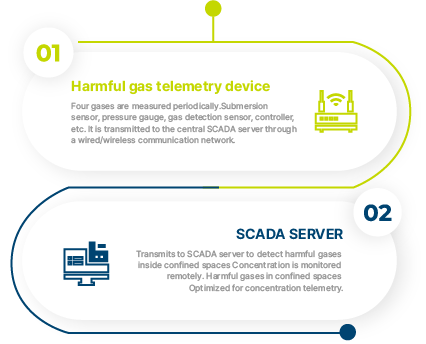
System Process
The IR-260G family of manhole confined space hazardous gas telemetry devices remotely monitors
the concentration of four gases - oxygen (O2), carbon dioxide (CO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and hydrogen sulfide (H2S)
- in the confined space of manholes located in the water supply system pipelines by periodically measuring and transmitting the data
to a central SCADA server via a wired or wireless communication network. SINNOTECH provides the best service by providing
products optimized for remote measurement of hazardous gas concentrations in confined spaces.
Area of Application

Remote Monitoring of Harmful Gases in Manholes
Measurement and remote monitoring of harmful gas concentrations inside confined spaces such as manholes in water supply, gas, electricity, and communication underground infrastructure.
Remote Monitoring of Harmful Gases in Industrial Plants
Measurement and remote monitoring of gas concentrations in areas prone to asphyxiation hazards in various industrial sectors such as livestock, sewage, chemical, and shipbuilding.